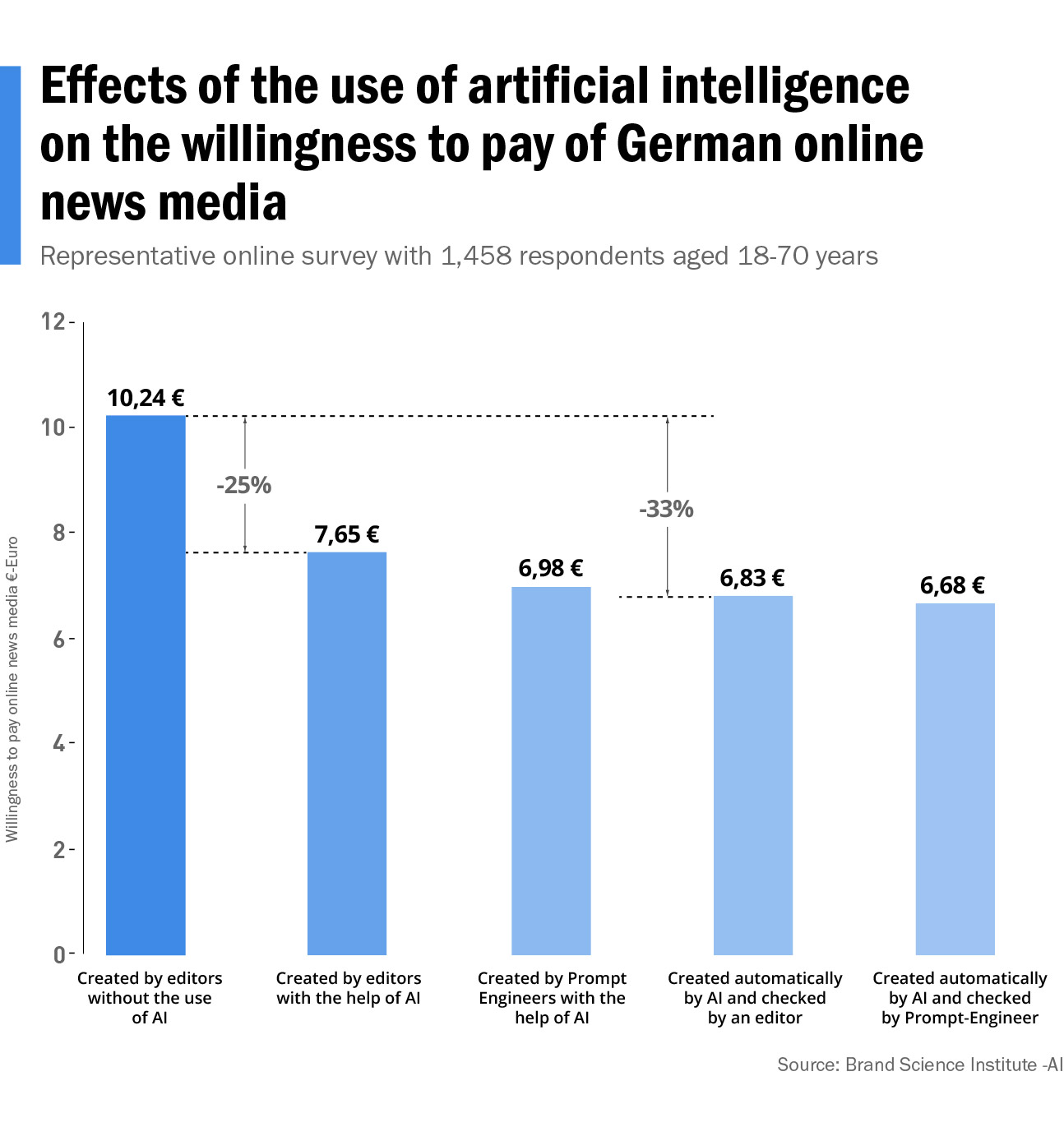
Users also differentiate between the extent to which AI is used for news production. Depending on whether artificial intelligence is used merely as an aid or for the fully automated creation of news and who operates the AI, the willingness to pay even falls by up to 33% depending on the type of AI used.
What results were generated?
General results
-
20% of respondents are generally willing to pay for online news
-
Increasing news consumption does not go hand in hand with a greater willingness to pay for online news.
-
The average willingness to pay among respondents is EUR 10.24, which is significantly lower than the average market price of EUR 17.38 for a monthly digital news subscription.
-
Respondents who have paid for online news in the last 12 months generally have a 15% higher willingness to pay.
Results on willingness to pay AI models
-
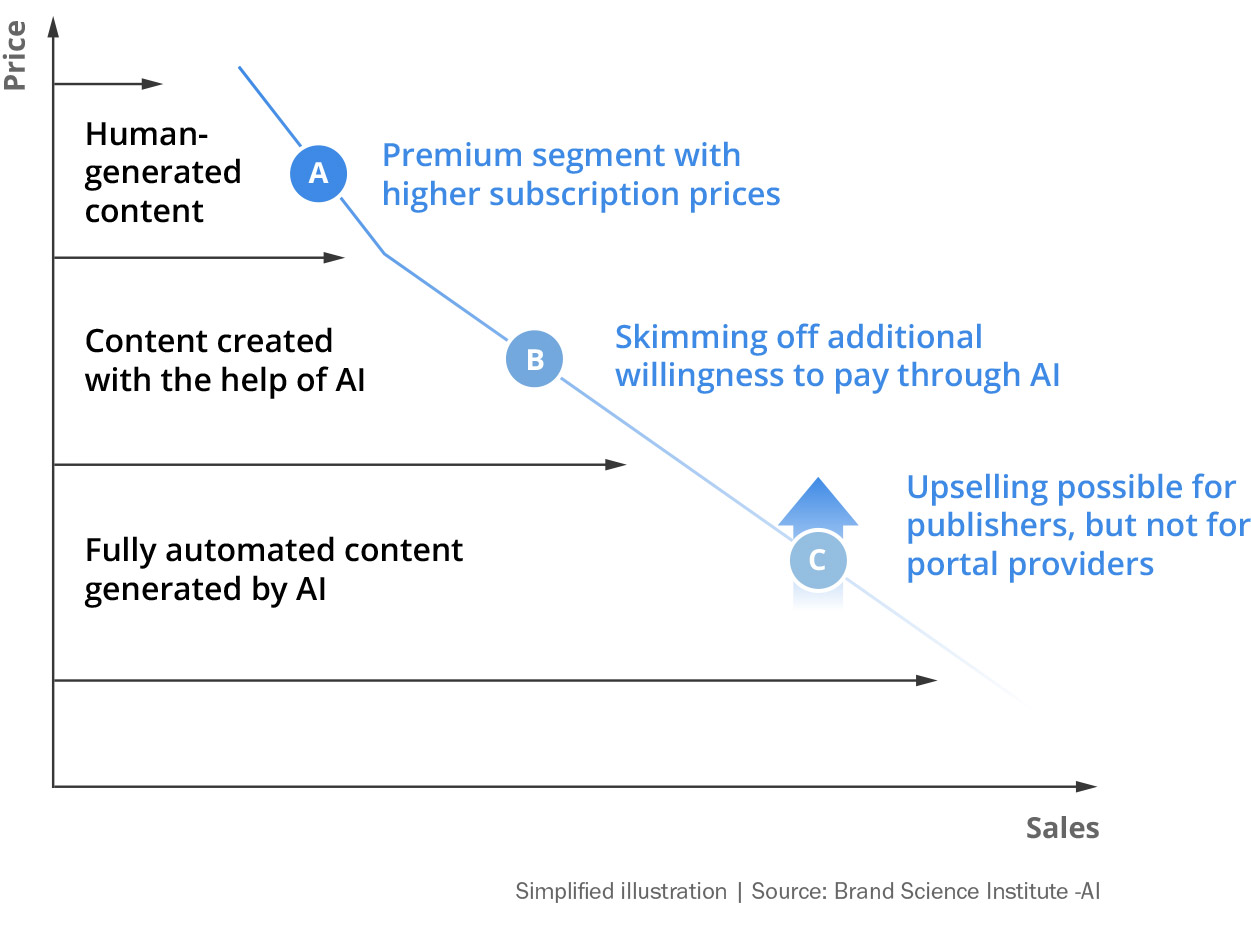
Among respondents who are generally willing to pay for online news, the willingness to pay for editorial content drops massively as soon as AI is used to research, process and create news.
-
The willingness to pay falls by up to 30% on average. Depending on the AI model used, the willingness to pay falls by up to 35%.
-
Among respondents who have paid for online news in the last 12 months, willingness to pay falls in the same proportion when different types of AI are used.
-
Familiarity and experience with AI have no influence on willingness to pay. AI amateurs and experts therefore show no difference in their willingness to pay.
Results on willingness to pay AI as a supporting tool
-
If AI is used as a supporting tool, the willingness to pay for content created by editors is around 10% higher than if it is created by AI experts (prompt engineers).
-
Confidence in the ability to develop high-quality editorial content with the help of AI is therefore attributed to editors.
-
The quality of the editorial articles created with the help of AI is rated higher by editors than that of Prompt Engineers in almost all areas of business, stock market & finance, science, sport, culture and politics.
-
Only in the area of weather do the respondents trust the prompt engineers to achieve the same high quality as editors in the AI-supported creation of news.
Results on willingness to pay AI fully automated
-
If AI is used for the fully automated creation of editorial content, the difference in willingness to pay between editors and prompt engineers becomes significantly smaller.
-
The AI expertise to create specific prompts is more appreciated by respondents in the context of fully automated and AI-generated content
-
Here too, however, the editor tends to generate a higher willingness to pay.
Studies by BSI AI
The BSI Group is one of the leading marketing services providers in Europe. With our "House of Marketing" and 193 employees in over 26 countries, we are active for our customers worldwide and deliver marketing services from a single source. Innovative marketing approaches and measurable success have been at the heart of our integrated marketing services for over 20 years.
All Studies